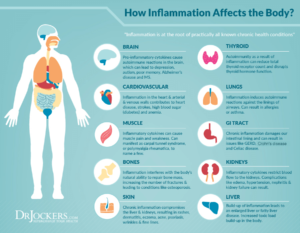
Inflammation is linked to almost all health conditions, with long term inflammation thought to be the root cause of many health problems.
It’s one of the many processes in our body that responds to infection (bacterial or fungal) or tissue damage. When something harmful affects our body, this biological response occurs to remove and heal it.
Acute inflammation usually appears as inflammation of the skin, and symptoms such as pain, redness, swelling and heat will appear.
You might be surprised to hear that inflammation can in fact be very helpful…
- It’s the bodies way of self-protection
- It’s part of our immune response
- It heals damaged tissue – an essential part of the healing process
However, chronic inflammation symptoms such as fatigue, mouth sores, chest pain, abdominal pain, fever, rash, and joint pain can lead to “dis-ease” and poor health conditions if not addressed.
Examples of conditions caused by chronic inflammation:
- Asthma
- Chronic peptic ulcers
- Tuberculosis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Periodontitis
- Colitis and Crohn’s disease
- Sinusitis
- Hepatitis
Learning to listen to your body and be aware of the signs are key to preventing long term illness
7 SIGNS OF CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
1. Chronic Fatigue
It is believed that chronic inflammation is directly linked to chronic fatigue.
Scientists have discovered a biological connection between the immune system’s inflammatory response and activity within the brain and spinal cord. This relationship enables chronic inflammation to interfere with the brain’s circadian rhythm, which controls sleep/wake cycles.
2. Red or Itchy Skin
High stress levels produce a large amount of inflammatory chemicals – and these can affect skin health. People with chronic skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis may see their symptoms exacerbate.
It’s also possible for chronic inflammation to cause acne or swelling and itchiness of the skin.
3. Excess Belly Fat
Excess belly fat may be a driver of inflammatory processes. Research has also discovered that environmental toxins, such as those found in processed foods, are linked to the degree of inflammatory response.
With findings such as these, it’s beneficial for us to reduce our process food intake, monitor our weight and consider shedding a few pounds if need be.
4. Digestive Problems
There’s an intricate link between the body’s levels of inflammation and digestive health. Frequent bouts of bloating, constipation, diarrhoea, gas, nausea or vomiting, are potential signs of an elevated inflammatory response.
It’s easy to fall into the trap of thinking that tummy problems are no big deal, and they may not be. However, if these problems are constant, it’s not normal – and may be an indication of an underlying health condition. Read more about IBS and what we can do to help here.
5. Food Intolerances
Sensitivity to certain foods is a common issue and one that kicks the immune system into overdrive. When this happens, inflammatory chemicals are released to ward off the food’s by-products and protect the person.
Dairy, gluten, eggs, grains, sugar, and corn are some of the big culprits of food intolerance. Fortunately, avoiding these foods will stabilise both the immune system and levels of inflammation. However ‘root cause’ of these intolerances should always be looked investigated
6. Headaches or Migraines
Persistent headaches are potential signs of higher inflammation levels. Similar to digestive problems, headaches may also be stimulated by toxins in the environment and in foods that cause inflammation.
Researchers have found a positive correlation (relationship) between migraine diagnosis cases and inflammatory markers within the body.
7. Depression or Depressive Symptoms
Depression and depressive symptoms are complicated, as many factors contribute to the condition. It may seem counterintuitive, but chronic inflammation may be one factor.
Many physicians have reached this conclusion by monitoring the frequency of people diagnosed with depression that also register with high levels of inflammation. These individuals are likelier to suffer from an inflammation-related health condition, such as Rheumatoid Arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
It’s important to remember that damaged tissue cannot heal without inflammation, however chronic inflammation can lead to disease.
Understanding the difference between acute and chronic inflammation is important.
Acute Inflammation vs Chronic Inflammation
Acute inflammation is caused by harmful bacteria and tissue injury. It occurs rapidly, lasts a few days, and either goes away or becomes chronic.
Chronic inflammation is caused by a virus, foreign substances/toxins, and an overactive immune system. It happens slowly, and can last months, even years. Chronic inflammation that is ignored can lead to internal tissue damage and scarred tissue.
How is Inflammation Treated?
Western medical treatments for inflammation are limited, but include:
- Steroid hormones that act on inflammation pathways, preventing its progression.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDS), such as Aspirin and Ibuprofen.
- Paracetamol is often taken but does not relieve inflammation.
These medications have a long list of side effects, and can actually promote inflammation with long term use.
How can a Nutritional Therapist help?
Diet, stress management and relaxation practices are essential to support lowering inflammation.
Using a functional approach we:
- Review your diet and make recommendations for an anti-inflammatory eating plan suitable for your current nutritional status
- Investigate and rule out underlying causes
- Review your lifestyle and make appropriate recommendations to reduce stress
- Recommend and arrange functional testing where necessary – testing takes out the guessing!
- Recommend best practice to support the body and mind to relax and reset
- Recommend treatment and services from our partners (if required), such as Osteopathy, Chiropractic, Acupuncture and Reiki.
Our bodies are complicated mechanisms made up of many systems that rely upon each other, but they’re also quite robust at the same time. Inflammation is our body’s way of telling us that something is wrong, and listening to it is the best way to put a stop to chronic inflammation.
If you or anyone you know are suffering with inflammation, get in touch, we can help.
Resources:
https://drjockers.com/chronic-inflammation/
https://draxe.com/health/inflammation/inflammation-at-the-root-of-most-diseases/